How Solar Power Works
Multiple Parts, One System
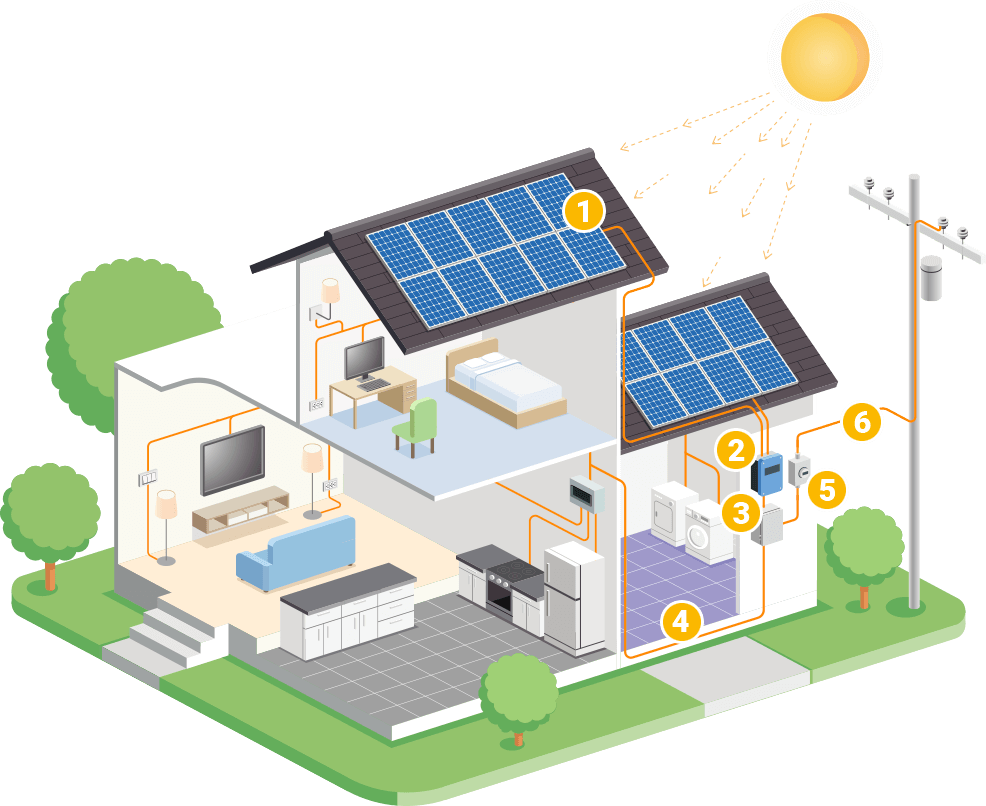
 Solar Modules
Solar Modules
 Inverter
Inverter
 Breaker Panel
Breaker Panel
 Home Electricity
Home Electricity
 Net Metering
Net Metering
 Grid Interconnection
Grid Interconnection
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Basics

SOLAR PANELS CONVERT SUNLIGHT INTO ELECTRICITY THAT CAN BE USED TO POWER YOUR HOME, ELECTRIC VEHICLE, OR COMMERCIAL BUILDING, AND ASSIST YOUR NEIGHBORHOOD’S POWER GRID.
Solar arrays are measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and vary widely in size depending on the demand of each building that needs to be powered. The number and efficiency of solar modules, their exposure to the sun, and available daylight hours are all factors that contribute toward sizing a system. We recommend talking to a solar professional to ensure that your system is sized and installed just right for you.
The average lifespan of a solar PV array is 30+ years, with low maintenance required.
How Net Metering Works
Sunlight charges the solar modules in a solar pv system, producing electricity during daylight hours. That electricity is used to power your home or business. If the system is sized for it, the modules can produce more electricity than is used by the connected building. When excess energy is created, it can be sent into the utility grid, which offsets your nighttime energy consumption. The interconnection between solar production and your power company can effectively cause your electric meter to run backwards and, if they have a policy for it, your utility provider may offer credits for excess power.
Sending electricity back into the grid this way is called ‘net metering’ and is offered by certain utility companies. Check with your provider for details. In those cases, customers are billed based on their net energy use. Simply put, net metering allows residential and commercial customers to use the grid as though it were an off-site energy storage system. It’s possible to produce more electricity than you use and receive a credit each month instead of a bill for your electricity usage.




Batteries And Solar Electricity Production

Charging Stations
